| |
| Fork Base Valve Percent [bv%] AND Shock Cadj Percent [ca%] |
- Shock ca%
- ca% = (ca force / c force)
- The compression forces are split between the shock mv and cadj piston.
- The amount of work done by each can be determined by ca%.
- The table on the right shows how the 'shock ca% value' is calculated.
- shaft area / (pist area - shaft area)
- In this case ca% calculates to 14.9%.
- Pressure testing allows us to split the shock compression forces into:
- how much from the main piston (c force)
- how much from the cadj piston (ca force)
- For any given velocity, c force should be about 85% and ca force 15%. This gives a quick snapshot showing if the cadj forces are in the ballpark.
- [click link for quick example]
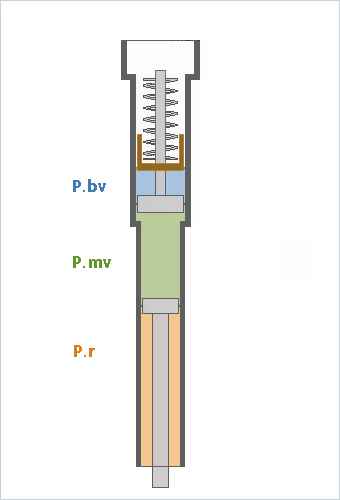
- Fork bv%
- bv% = (bv force / mv force)
- The table on the right shows how 'fork bv% value' is calculated.
- rod area / (pist area -rod area)
- In this case bv% = 14.6% for the YZ 250 and 22.5% for the XCF 350.
- Unfortunately, bv% does not work the same as ca%.
- Pressure testing allows us to split the fork compression forces into:
- how much force from the mv piston (mv force)
- how much force from the bv piston (bv force)
- Shock ca% will always be around 15% and can be used as a guideline when valving the cadj.
- But bv% cannot be used as a guideline. Long travel and reliance on stiff bv force puts bv% as high as 600%.
- [click link for quick example]
|
 |
|
|
|
| |
Untitled Document
|
|
|
bv% value = rod area / (pist - rod area) |
| |
bv% = (bv force / mv force) |
|
| bv% (113/503) |
22.5 %
|
pist dia
rod dia
pist area
rod area
pist - rod area |
28
12
616
113
503
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
 |